A recent study published in JAMA Surgery highlights the benefits of normothermic machine perfusion (NMP) in liver transplantation, particularly for organs from donation after circulatory death (DCD) donors. NMP involves preserving donor livers at body temperature with continuous oxygenated blood flow, which maintains organ viability and function.
In a retrospective analysis of 1,086 adult liver transplant recipients at the Mayo Clinic in Arizona (2019–2023), researchers compared outcomes between livers preserved with NMP and those with traditional static cold storage (SCS). The findings revealed that NMP-preserved DCD livers had the lowest rates of early allograft dysfunction and led to shorter hospital and ICU stays compared to SCS-preserved livers.
These results suggest that NMP not only improves immediate post-transplant outcomes but also has the potential to expand the donor pool by making more DCD livers viable for transplantation. However, the study’s authors note that further research is needed to fully understand the long-term benefits and to establish standardized protocols for broader application.
SOURCE: https://www.healio.com/news/gastroenterology/20250303/normothermic-machine-perfusion-boosts-liver-transplant-outcomes-may-expand-donor-criteria
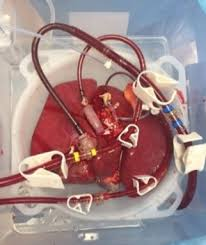
Does Machine Perfusion Improve Outcomes?
Machine perfusion, or “liver pump,” refers to the technology associated with preserving organs during the transplantation process with circulating perfusate that mimics blood flow.
There are several ongoing randomized control trials assessing machine prefusion for liver transplantation though much of the current evidence is from cohort studies. The evidence from past studies does suggest benefit over static cold storage.
A Cochrane review with seven randomized trials showed potential benefit as well with three trials considering normothermic machine perfusion and four into hypothermic machine perfusion. There was no statistical improvement in mortality found and no quality of life data reported. And yet, with hypothermic machine perfusion there was improved graft survival and decreased adverse events in extended criteria grafts, as well as improvement in clinically significant ischemic cholangiopathy in recipients of DCD livers, compared to SCS. And normothermic machine perfusion was associated with improved utilization in grafts that would be otherwise discarded, though this result is undergoing further study.
