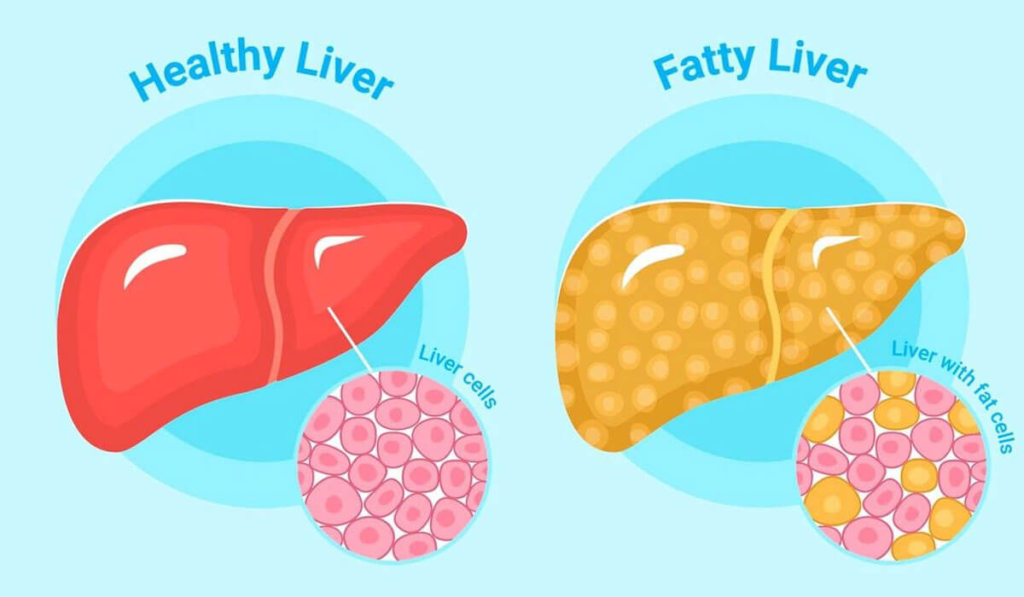
Broadly, there is a form of Fatty Liver Disease that is associated with alcohol use (ALD for Alcohol-associated Liver Disease) and a form that is NOT associated with alcohol use (NAFLD for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease).
And of late, we now have MASH and MASLD as names with more specificity.
MASH stands for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis, and MASLD stands for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
These names actually replaced two previous terms, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). And the new names were chosen to eliminate stigma and better describe the diseases.
MASH is a more serious stage of MASLD, where the liver is inflamed and damaged. MASH can lead to liver failure or liver cancer in some people.
MASLD is an umbrella term for conditions where the liver has too much fat, but it’s not caused by alcohol. MASLD is linked to obesity, type 2 diabetes, and other conditions.
The risk factors include Obesity, Type 2 diabetes or pre-diabetes, High levels of LDL cholesterol, and Metabolic syndrome.
