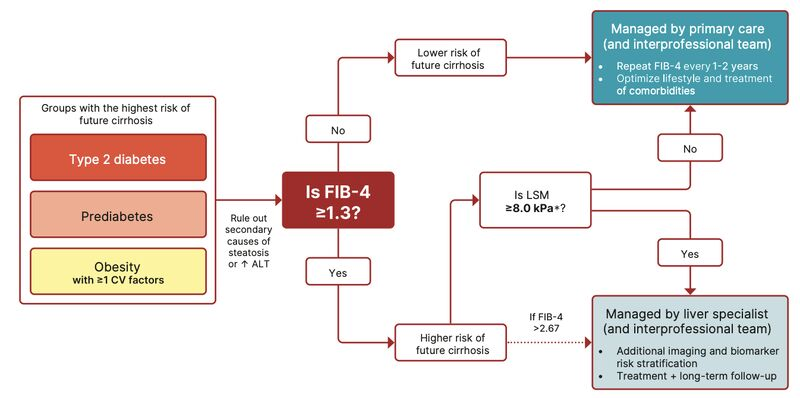
An article recently published in Diabetes Care highlights the significant interplay between metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and type 2 diabetes.
Summary–
🔄 Bidirectional Relationship Between MASLD and T2D
- Prevalence: Approximately two-thirds of individuals with T2D also have MASLD
- Impact of MASLD on T2D: MASLD contributes to increased insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia, leading to poorer glycemic control in T2D patients.
- Impact of T2D on MASLD: T2D accelerates the progression of MASLD, increasing the risk of advanced liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma .
⚠️ Clinical Implications
- Increased Morbidity and Mortality: The coexistence of MASLD and T2D elevates the risk of liver-related complications and cardiovascular diseases.
- Need for Integrated Care: Healthcare providers should adopt a multidisciplinary approach, incorporating regular liver assessments in T2D management plans.
🩺 Recommendations for Healthcare Providers
- Routine Screening: Implement regular screening for liver steatosis and fibrosis in patients with T2D.
- Lifestyle Interventions: Encourage weight management, healthy diet, and physical activity to mitigate risks associated with both conditions.
- Pharmacological Considerations: Consider medications that address both glycemic control and liver health.
In summary, the article emphasizes the critical need for heightened awareness and proactive management strategies to address the intertwined nature of MASLD and T2D, aiming to improve patient outcomes through comprehensive care.
SOURCE: diabetesjournals.org+2researchgate.net+2touchendocrinology.com+2